Definition
Urea is the chief nitrogenous end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in all mammals and some fishes. It occurs not only in the urine of mammals but also in their blood, bile, milk, and perspiration.
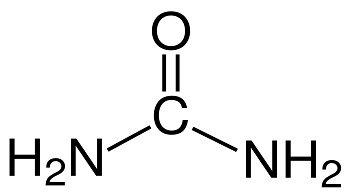
Urea, also called carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CH₄N₂O. This amide has two amino groups joined by a carbonyl functional group. It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid

Application of urea:
It is used as a raw material for the production of urea-formaldehyde and urea-melamine-formaldehyde resins.
Urea is also used to produce plywood.
It is also used as a stabilizer of nitrocellulose explosives.
Urea has important uses as a fertilizer and food supplement, as well as a raw material for the production of plastic and medicine.
It is an element in diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) that contains 32.5% urea and 67.5% deionized water. DEF is injected into the exhaust stream of diesel vehicles to break down dangerous NOx emissions into harmless nitrogen and water.
A component of animal feed, it is a relatively inexpensive source of nitrogen to promote growth.
It is considered a non-corrosive alternative to rock salt for road de-icing. It is often the main ingredient in pet-friendly salt alternatives, although it is less effective than traditional rock salt or calcium chloride.
It is a main ingredient in the formulation of hair removal compounds.
It is one of the reasons for the brown color in the cans produced in the factory.
It is an ingredient in some skin creams, moisturizers, hair conditioners and shampoos.
A flame retardant, commonly used in dry chemical fire extinguishing charges such as a mixture of urea and potassium bicarbonate.
It is an important ingredient in the formulation of many teeth whitening products.
It is one of the raw materials for the production of dishwashing soap.
It is used together with diammonium phosphate as a yeast nutrient to ferment sugars into ethanol.
Nutrient used by plankton in ocean feeding experiments for geoengineering purposes.
It is used as an additive to increase the working temperature and opening time of skin glue.
It is used as an additive for solubility and moisture retention in dye baths for dyeing or printing fabric.
It is used as an optical parametric oscillator in nonlinear optics.
Urea is a raw material that is used in the manufacture of many chemicals such as various plastics, urea-formaldehyde resins and adhesives.
Also, industrial urea is necessary for the production of raw materials, glue, fertilizer, commercial products and resin production.
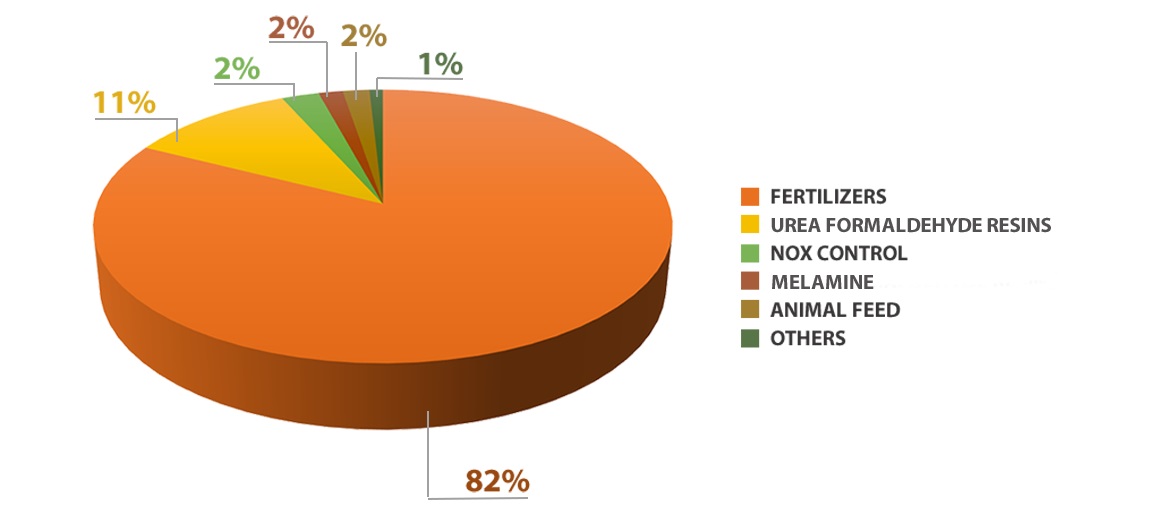
Application of urea in agriculture:
More than 90% of the world production of urea is intended for use as a nitrogen-releasing fertilizer. Urea has the highest amount of nitrogen among all solid nitrogen fertilizers in common use. The most common impurity is artificial urea biuret, which disrupts plant growth. Urea decomposes in the soil and gives ammonium. Ammonium is absorbed by the plant. In some soils, ammonium is oxidized by bacteria to nitrate, which is also a plant nutrient. The loss of nitrogenous compounds harms the atmosphere and waste runoff and the environment. For this reason, urea is sometimes pre-treated or modified to increase the efficiency of agricultural use. One of these technologies is controlled release fertilizers that contain encapsulated urea in an inert seal. Another technology is the conversion of urea into derivatives such as formaldehyde, which decomposes into ammonia at a rate corresponding to plant nutrition.
The best way to use urea in agricultural products is to mix it with water. Because urea dissolves easily in water. Therefore, with uniform irrigation by mechanized irrigation devices, it is possible to feed the plant to the required amount.
Due to the high nitrogen content of urea, it easily turns into soil. Therefore, it is widely used to prepare fertilizers. The way of using agricultural urea is in such a way that they either put it in the soil or pour it on the leaves. It is necessary to know that urea nitrogen is non-protein, but it can be used in the feed of ruminant animals such as sheep and cattle.
Urea fertilizer can also be used in crops, cereals, wheat or other small grains. Therefore, it should be done in cold seasons, because due to heat and heat, urea destroys ammonia, and if it is done in summer, it should happen when there is a high probability of rain.

Urea Types
Two types of urea include prilled and granules are widely used as fertilizers. They are produced from the reaction between ammonia and carbon dioxide.

Prilled urea is a form of nitrogen-rich solid fertilizer that has the ability to dissolve quickly in water.
Prilled urea is more commonly used today to resist breaking down when mixing with other fertilizer components like Potassium chloride.
It is also known as ice melting or deicing urea since it can reduce ice efficiently, even at very low temperatures ( -6 ◦C). The urea prill has a high resistance. This makes urea fertilizer remain longer and we don’t need to use fertilizer in short periods of time.
Granular urea has bigger particles and an uneven shape. It is stronger than prilled urea and less likely to break. It can be applied directly to the soil or mixed with other fertilizers like phosphate and potash to create a complete food mix for plants.
This type of urea can be easily applied using conventional spreading equipment.
Urea fertilizer is mostly utilized for bloom growth because it can only offer nitrogen and neither phosphorus or potassium.
Urea is a crystal that is white in color. It is a nitrogen fertilizer as well as a simple organic molecule. Urea is simple to store, utilize, and doesn't harm the environment.
At the same time, urea is one of the most extensively used chemical nitrogen fertilizers, as well as the primary raw ingredient in the NPK fertilizer manufacturing process.
Urea should not be spread on the ground because of its disadvantages. Disadvantages of Urea are:
1. Only after 4-5 days of transformation at room temperature may urea be used. In the ammunition process, the majority of the nitrogen is easily volatilized. In most cases, the real utilization rate is only around 30%. If urea is sprayed onto soil which is alkaline and has a high concentration of organic matter.
2. Fertilizer damage is easily caused by too much urea. Because urea has a high nitrogen content, it should not be used in excess to avoid waste and fertilizer damage. Many farmers in fruit-producing areas use a lot of urea, which kills trees and has catastrophic implications.
3. Urea must be used ahead of time because it takes a long time to take effect. We must be aware of how urea decomposes in the soil when it is applied as a top dressing. Urea must be converted into ammonia nitrogen about 7 days after application to offer a fertilizer effect. Urea fertilizers for home plants "provides excellent effect on overall plant growth, encourages the growth of shoots/leaves and improves the shelf life of the produce. Weight: 400 gr water-soluble helps the plant set buds and flowers".
In terms of the environment, the production of urea involves the discharge of numerous toxic chemicals into the atmosphere. Furthermore, urea (particularly urea nitrate) is a volatile material that might explode if kept improperly or without monitoring.
Note:
The skin, eyes, and respiratory tract can all be irritated by Urea. Dermatitis can be caused by repeated or extended contact with urea in fertilizer form on the skin. Blood concentrations that are too high can be harmful.